
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Computer Graphics and Programming
Lecture 5
Extended Primitives
Jeong-Yean Yang
2020/10/22
1
T&C LAB-AI
Ground, Axis, and so on.
1
2
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
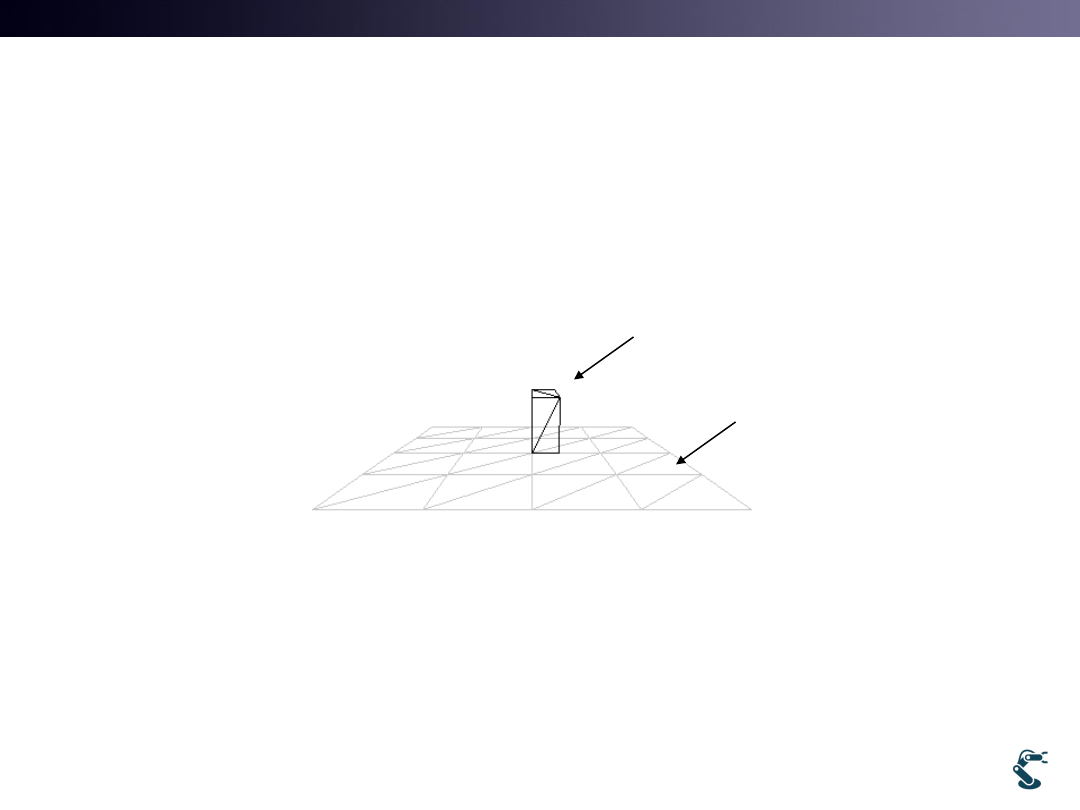
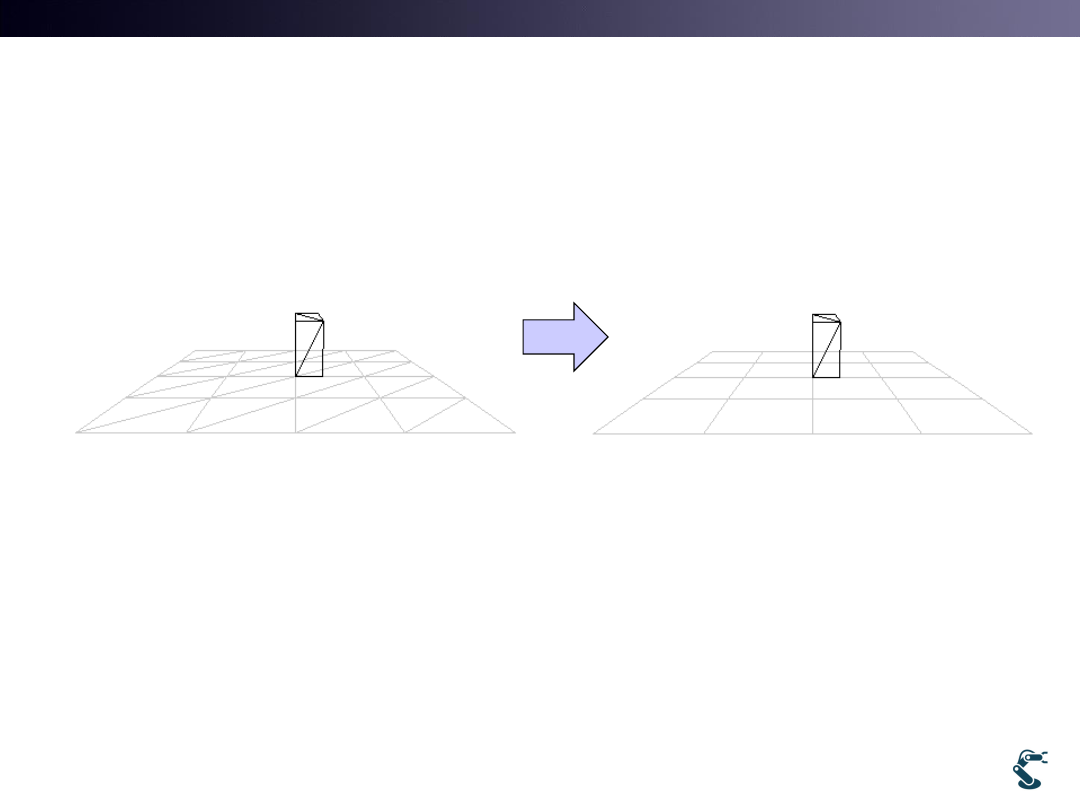
Ground Modeling
• 3D Environment is confused.
– Ground( Grid plane) is helpful for intuitive understanding.
• Extending uObj::MakePlane in Ch. 3
3
Object
Ground
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
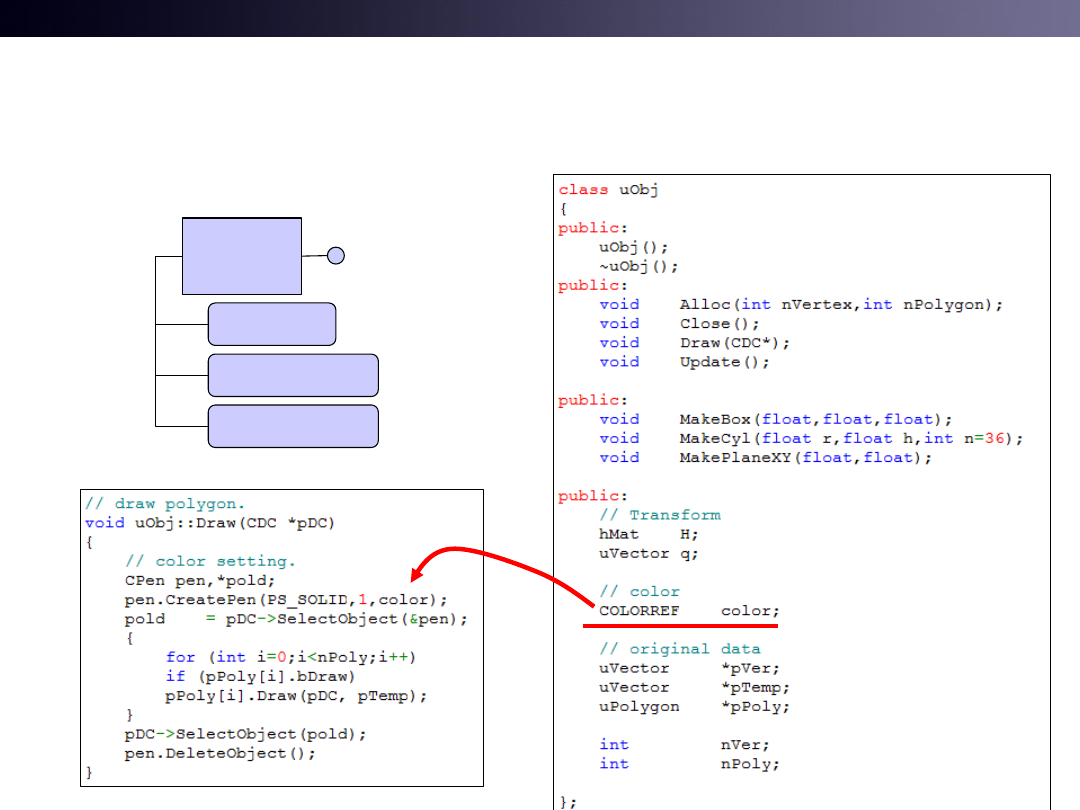
Color for Ground Object
ex) uWnd-31-Ground-Triangle
4
uObj
MakeBox
MakeCylinder
MakePlane
color
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
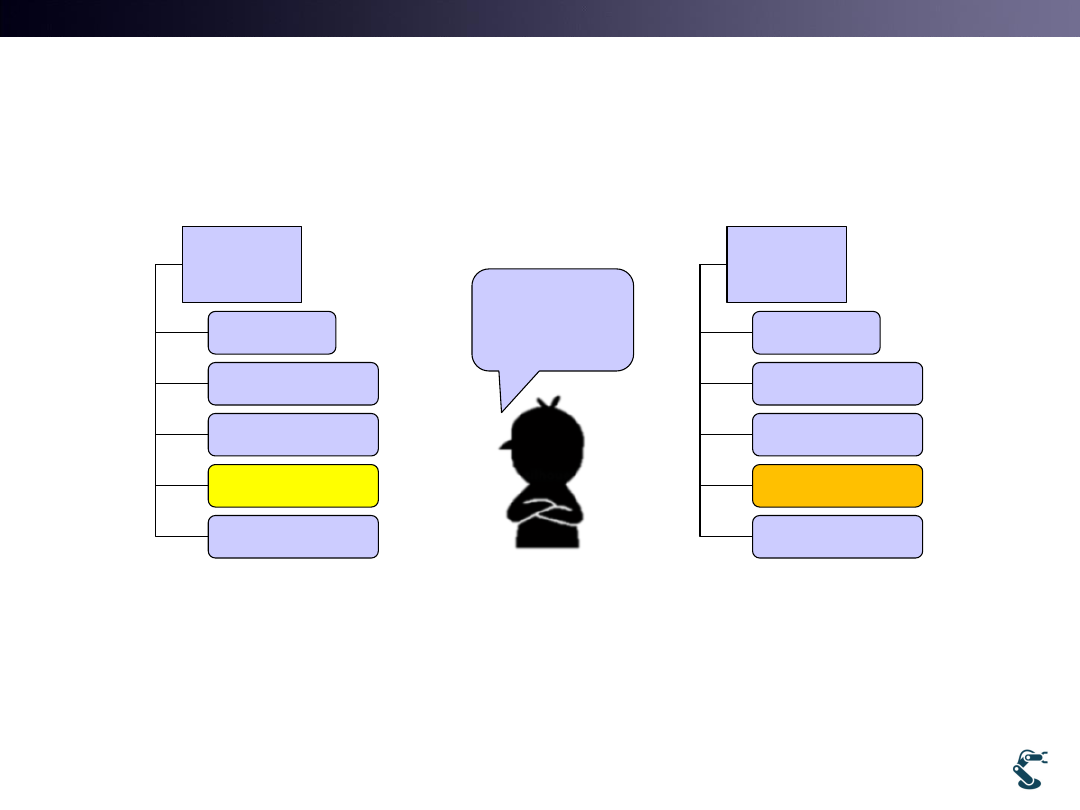
Question: If we modify Ground Object,
How can we do?
• We MUST modify uObj class
• Lets redefine uGround class by subclassing uObj
5
Look better
uWnd-31-Ground-Triangle
uWnd-32-Ground-Quad
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Wrapper Class
(Subclassing Class+ Overriding function
Inheritance)
• C++ has been popular with Subclassing Technique.
6
uObj
MakeBox
MakeCylinder
MakePlane
Draw Triangle
Update
uGround
MakeBox
MakeCylinder
MakePlane
Draw Quadratic
Update
Slight
Change !!
??
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Wrapper Class
(Subclassing or Inherited Class)
• uGround is inherited by uObj
– uGround has every features of uObj.
7
uObj
MakeBox
MakeCylinder
MakePlane
Draw Triangle
Update
uGround
Draw Quadratic
uObj
Inheritance
Class uGround: public uObj
uGround ground
ground.MakeBox (o)
ground.Draw
(o)
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
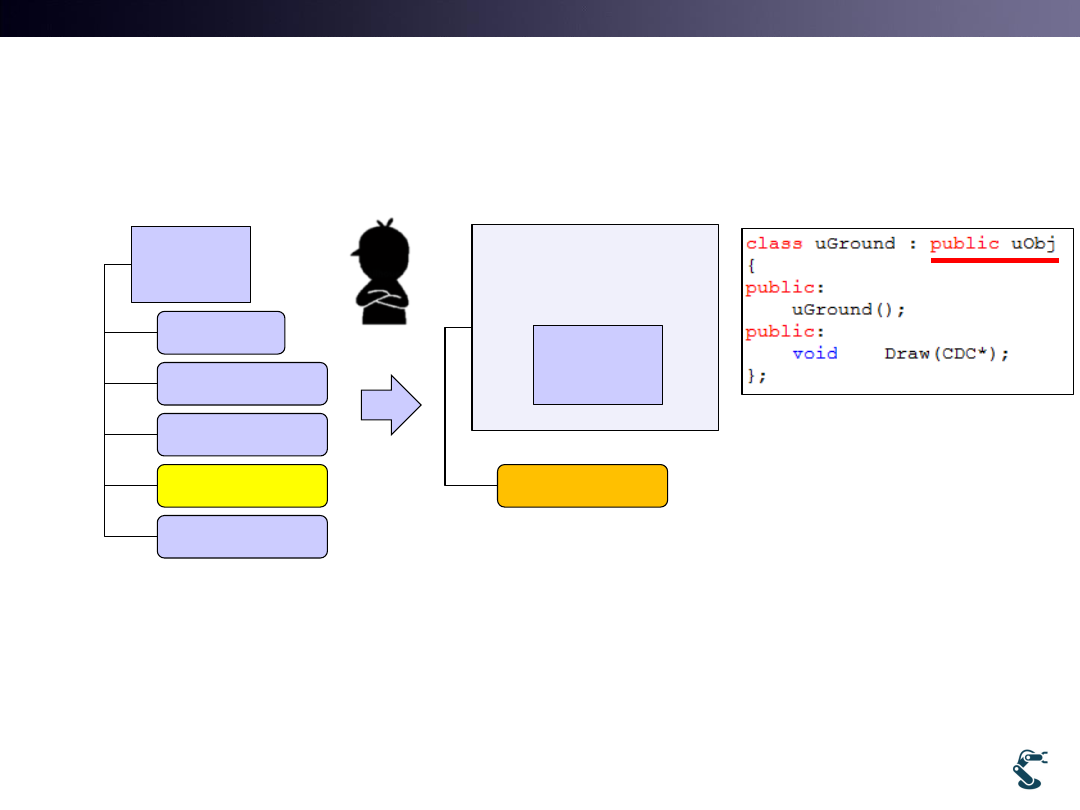
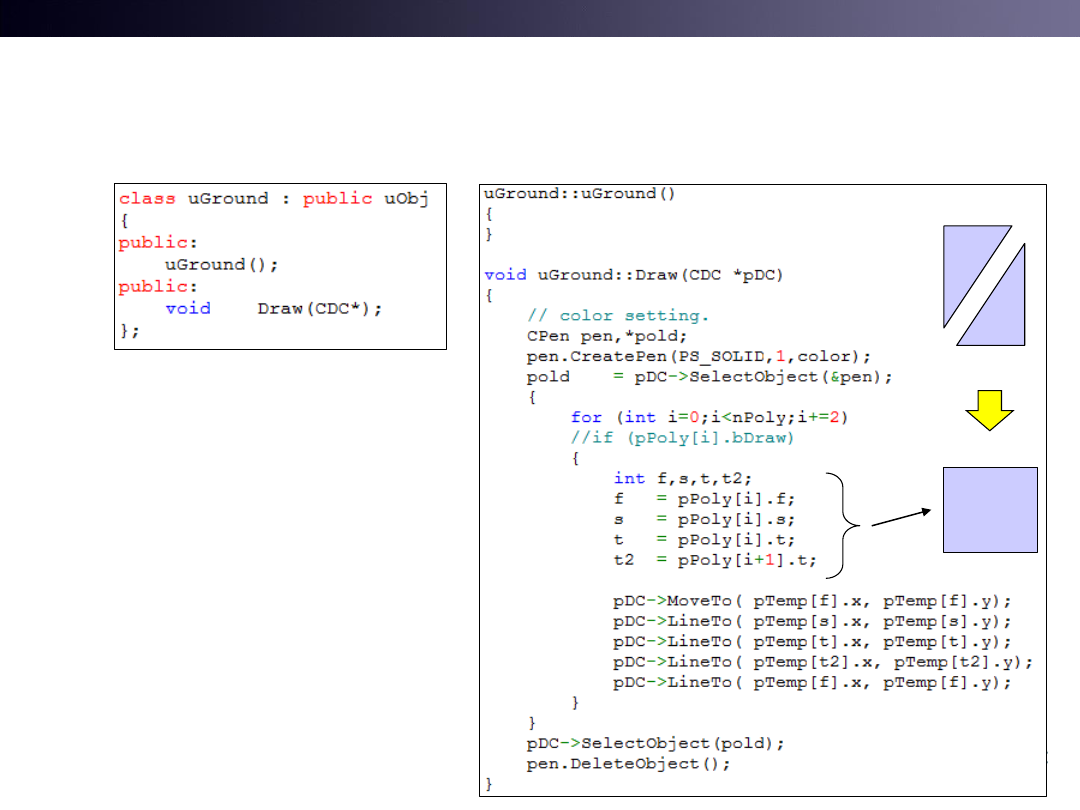
Only Modify uGround::Draw
ex) uWnd-31-Ground-Quad
• uObj::Draw()
– Draw two triangles
• uGround::Draw()
– Draw one rectangle
8
f
s
t
f’
s’
t’
f
s
t
t’
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
XYZ Axis Modeling
• Axis is also helpful for understanding 3D environment.
9
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
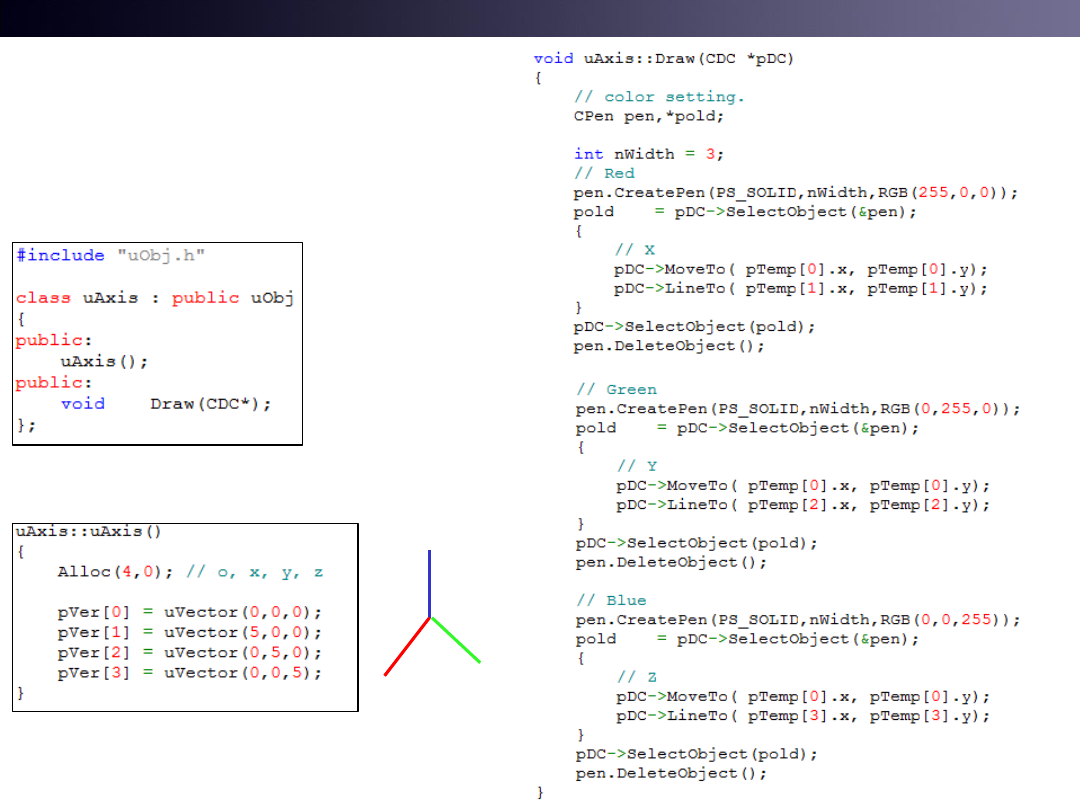
uAxis from uObj
Refer to uWnd-32-Axis
• Subclassing uAxis from uObj
10
Subclassing uObj
4 vectors are needed
O(origin), x,y,z
pVer[0] :o
pVer[1] :x
pVer[2] :y
pVer[3] :z
pTemp[0]: o in 2d
pTemp[1]: x in 2d
pTemp[2]: y in 2d
pTemp[3]: z in 2d
o
x
y
z
Line o to 1
Line o to 2
Line o to 3
T&C LAB-AI
Multiple Objects
2
11
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
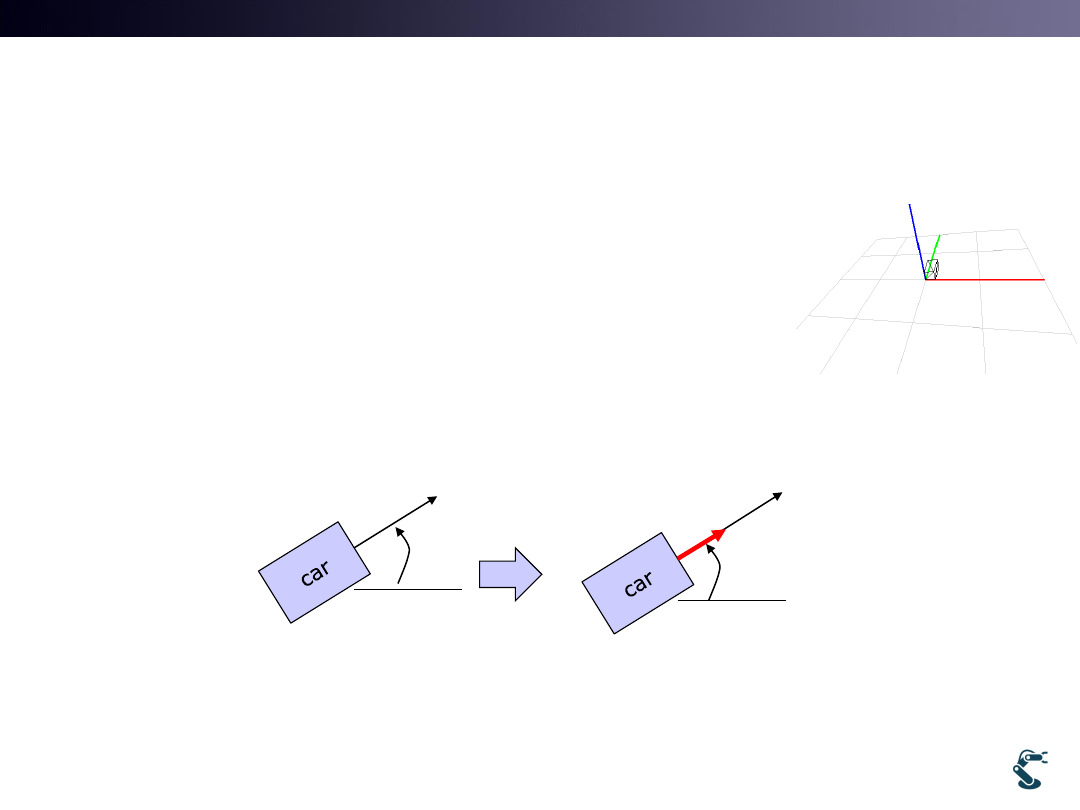
Extending into Multiple Object
• How to transform Multiple Object?
• Let’s think a Car
– uWnd-34-Car1 with KEY input for acceleration
12
v: velocity
W: angular velocity
v
w
Dir: direction vector
Vel: speed
V = dir * vel
dir
v
:
atan2( . , . )
( )
heading angle
v y v x
RotZ
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
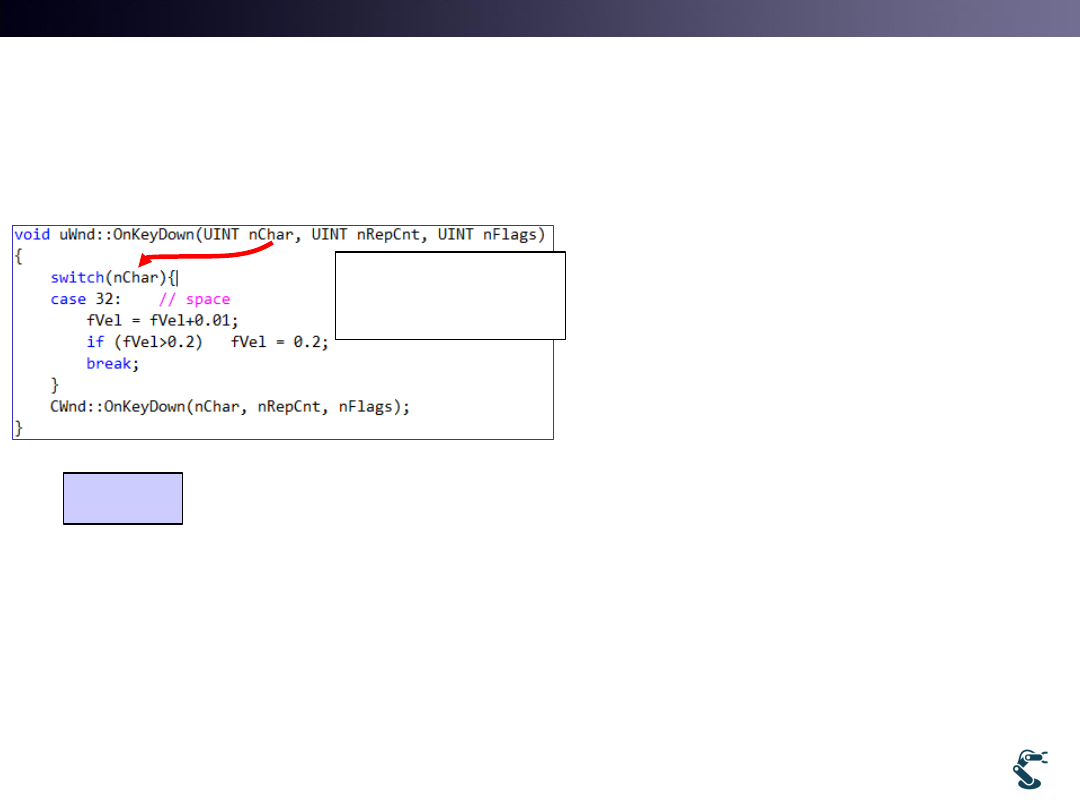
Key Input
• If you press a space key,
– Vel Vel + 0.01
• Limitation of Maximum
speed
– If (Vel>0.2) Vel = 0.2
13
car
uVector dir(0,1,0) direction vector with heading angle
float fVel = 0; Car’s velocity
When space key is
pressed,
Velocity increases.
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
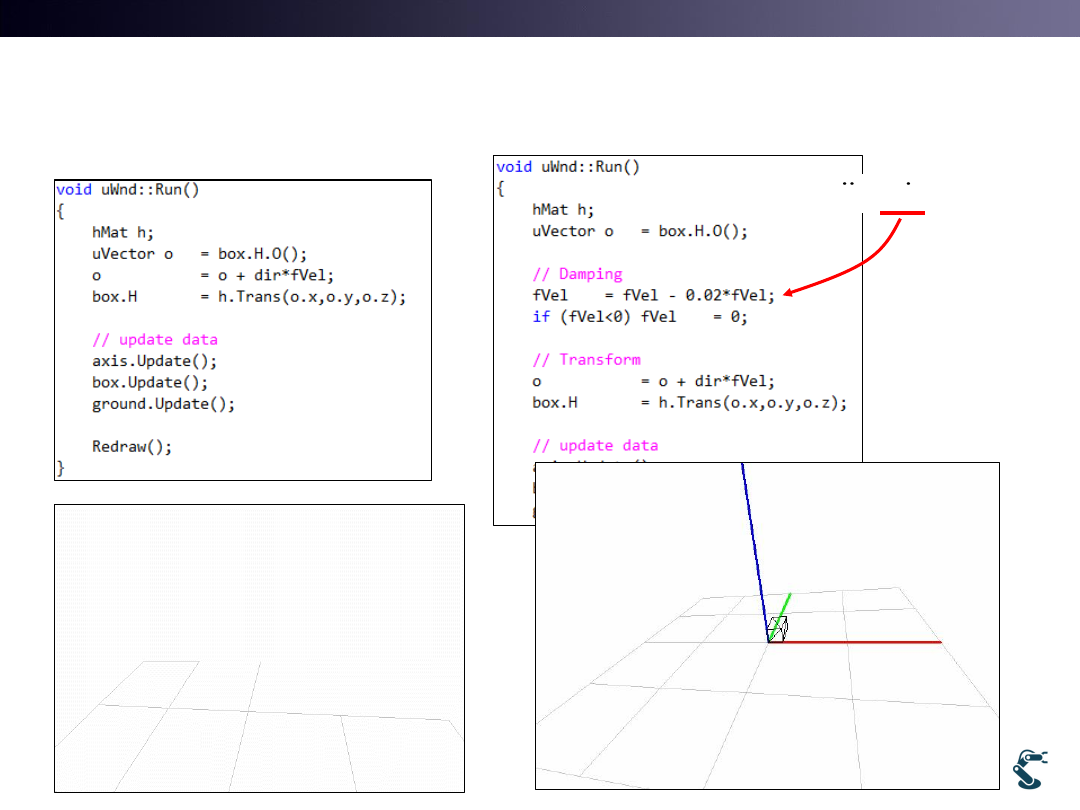
Car Moving with a Velocity and Damping
14
mx cx
kx
F
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
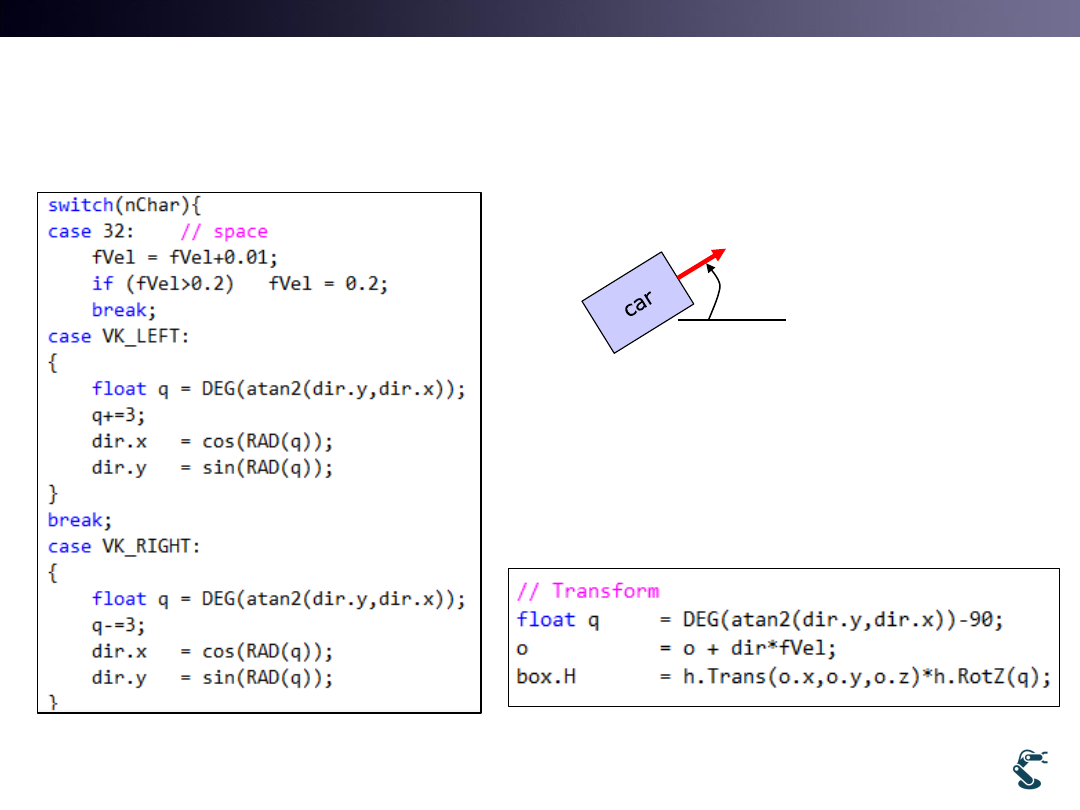
Car Navigation by
Pressing Left-Right Key for direction change
uWnd-35-Car2
• Left +3 deg, Right -3 deg
Counter clock wise along Z
15
dir
:
atan2( . , . )
heading angle
v y v x
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Example: uWnd-35-Car2
16
RotZ is NOT done at the center
HW 5,8, 9 !!
If we Add Wheel,
Multiple Object Car
Will be very complex
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
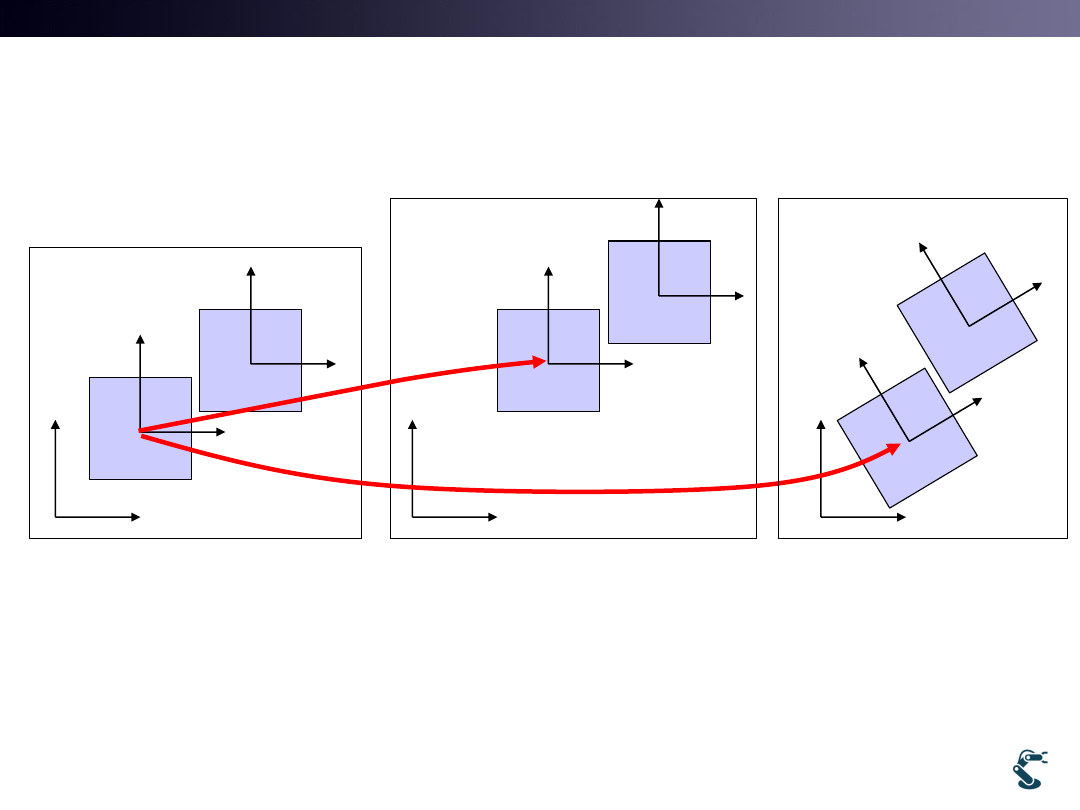
Multiple Object:
An Object has other Objects
• When Parent, P moves, Child, C also moves.
• Translation is Easy but Rotation is More complex
• We need to design Hierarchical Approach
17
Translation
Rotation
P
C
P
C
P
C
P: parent
C: child
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
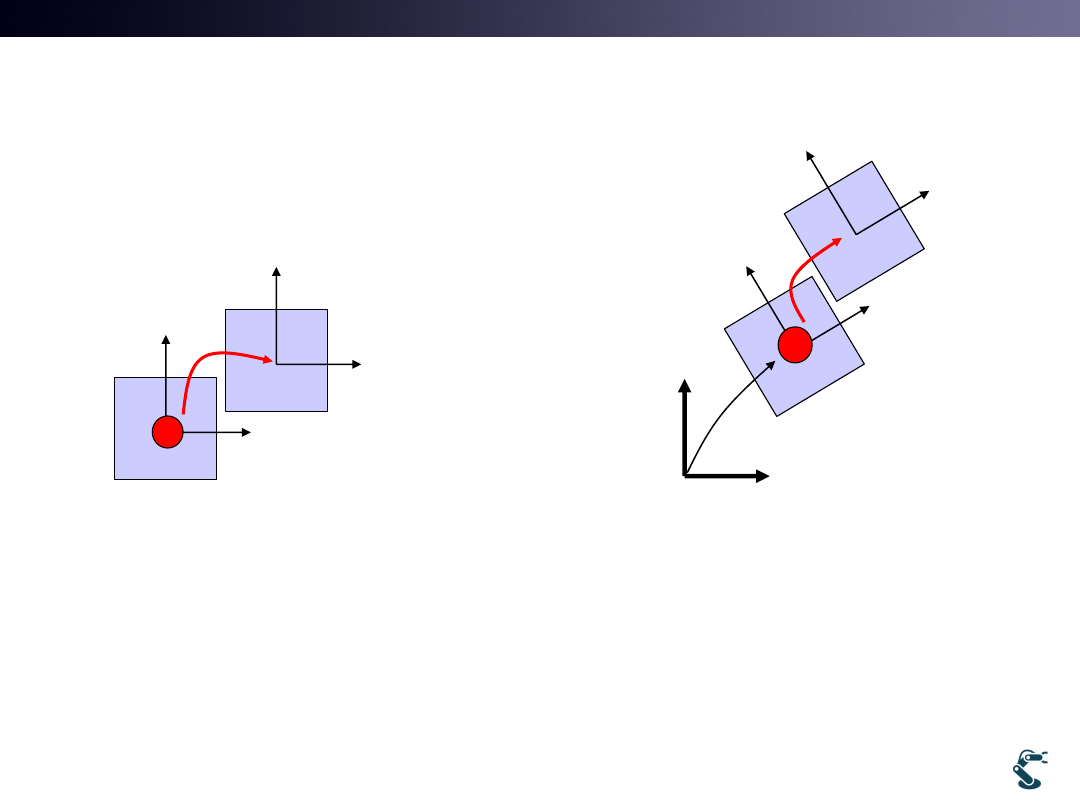
Child has the Relative Transform, H
w.r.t. Parent
18
H
Hg’
H
P
C
Relative
transform
g
current
g
current
g
H
I
P
H P
P
H
C
H
C
H
C
'
'
'
g
g
current
g
current
g
H
H
P
H
P
C
H
C
H
• Child’s Relative Transform, H is constant
Child looks fixed on Parent.
Parent is on origin.
If parent moves,
Child also moves
P
C
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
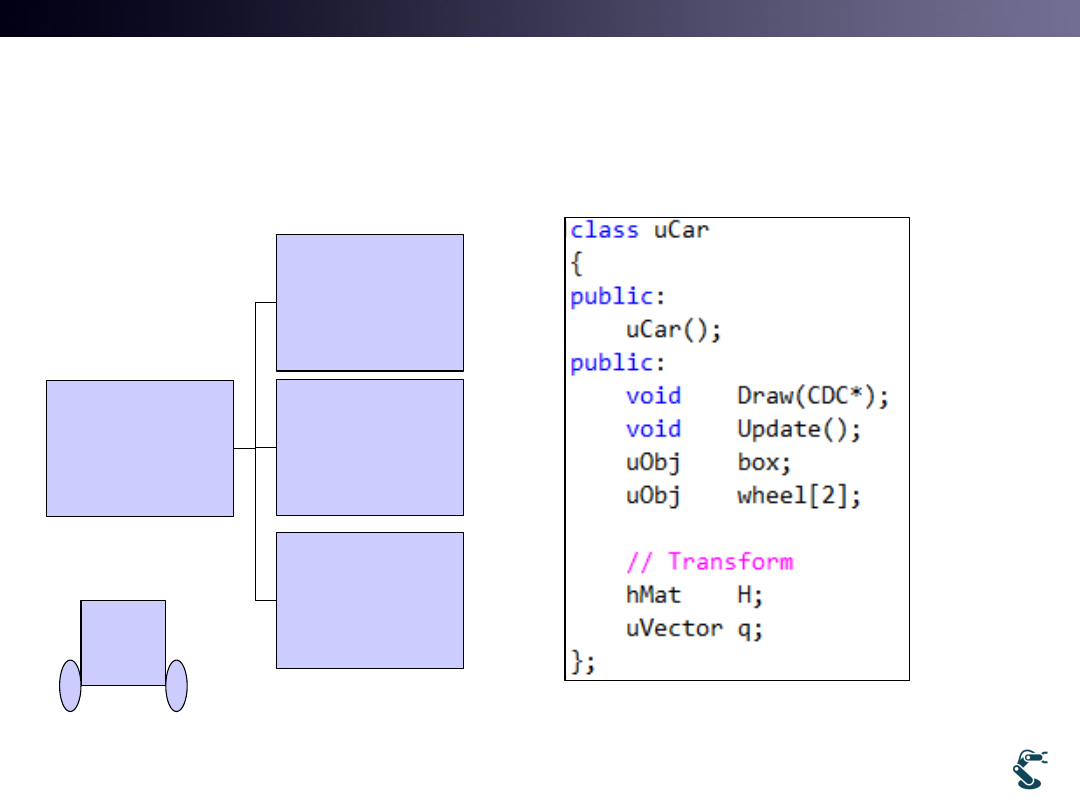
Extending uObj into
Multiple Object, uCar Class
19
uCar
H ( Hg)
uObj
H
Box
uObj
H
Left Wheel
uObj
H
Right Wheel
box
Left
Wheel
Right
Wheel
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
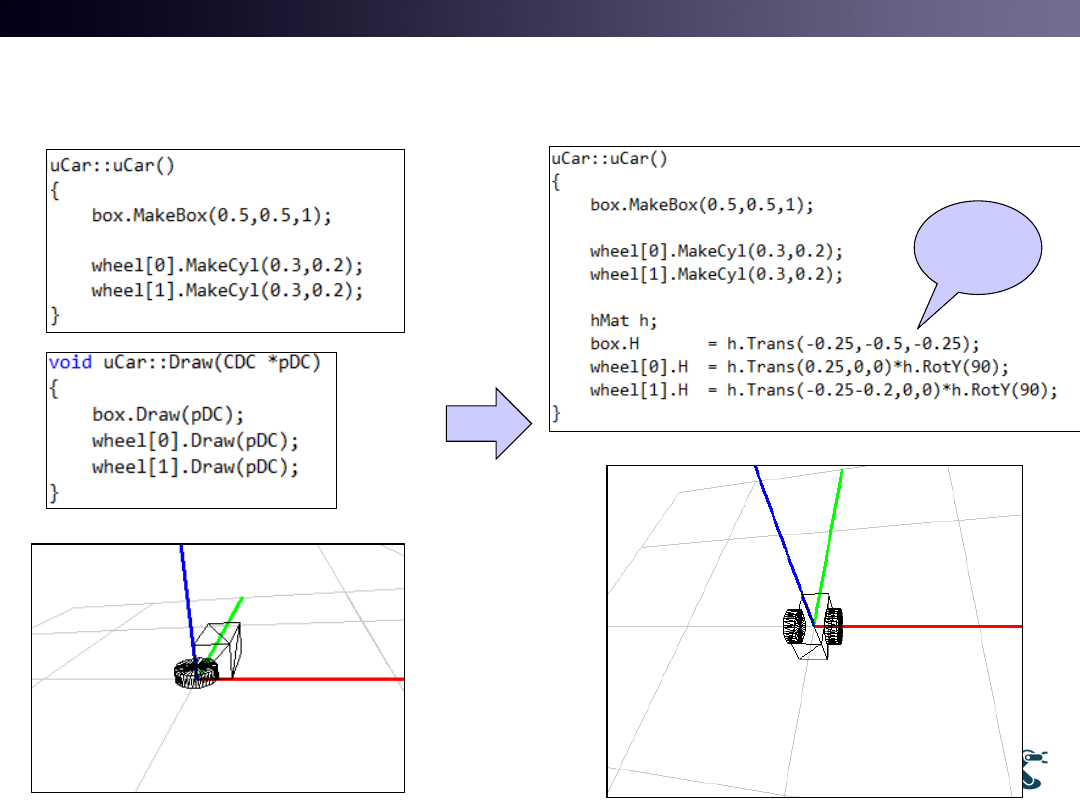
uCar Geometry Design
20
Initial
Setting
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
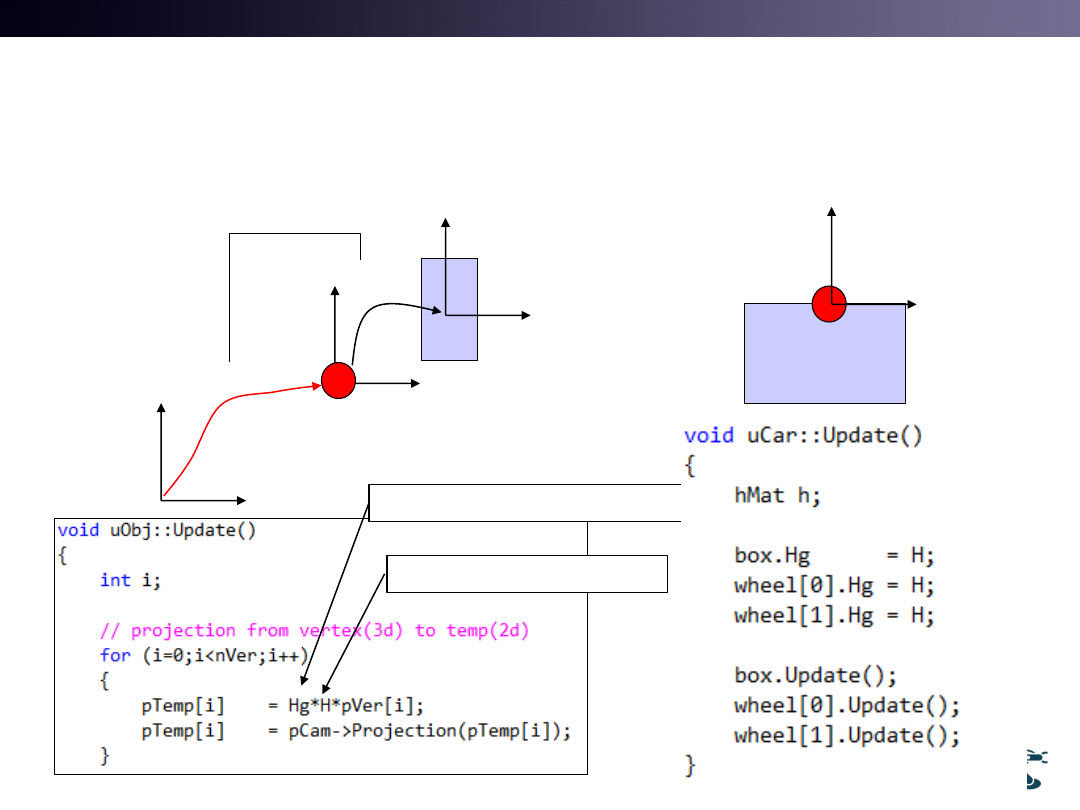
uObj
::Update() Has Parent’s Transform
21
Hg
H
Parent’s Transform : Hg
Self Transform : H (Hrel)
V’=Hg*H*V
uCar::H
Hg
Box, wheels
uCar
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Example: uWnd-36-Car3
22
T&C LAB-AI
Object Skeleton from Multiple
Object
3
23
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
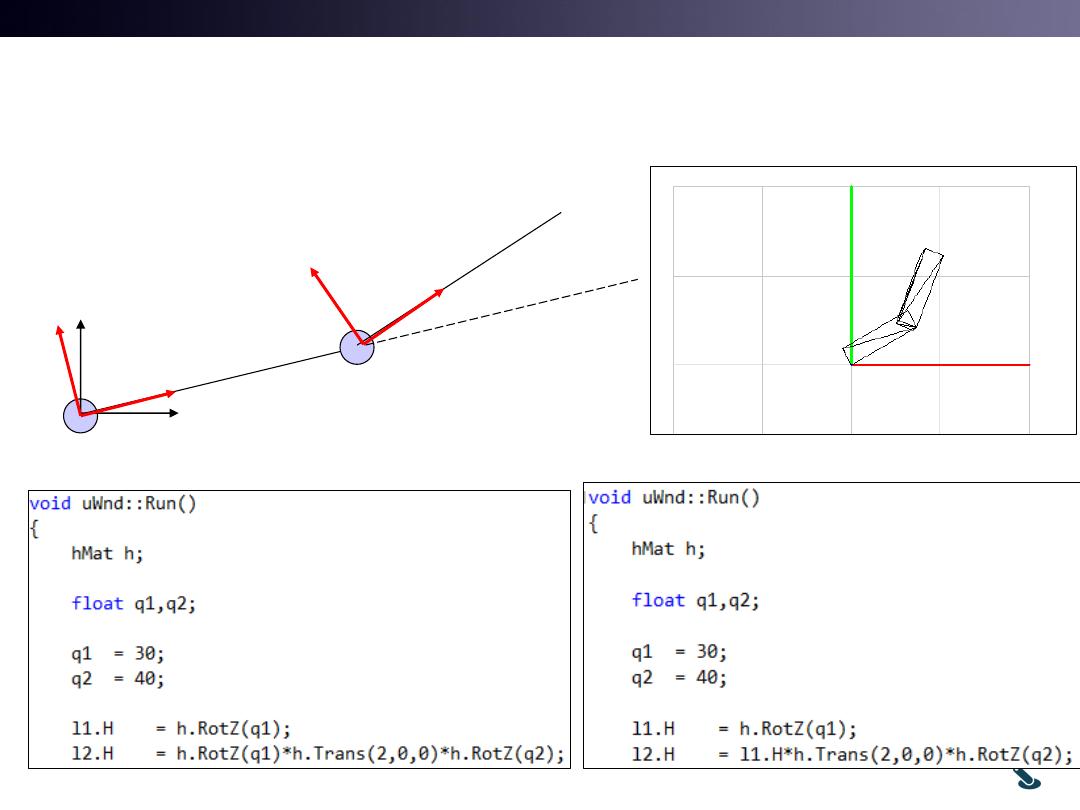
Multiple Object for Robot Arm
uWnd-37-Robot
24
X
Y
?
1
1
l
2
l
2
(x,y)
X
Y
0
1
2
3
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
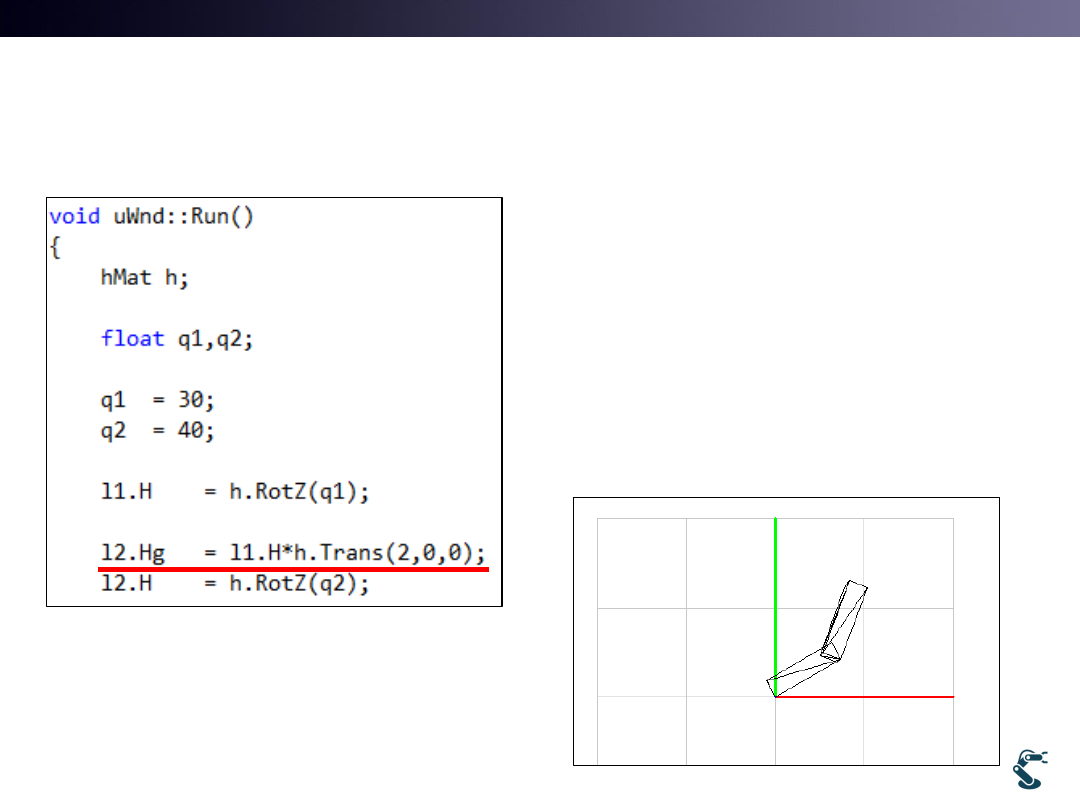
Multi Object with uObj::Hg
uWnd-38-Robot
• Hg is Parent Object’s
Transform.
• l1.H and l2.H are regarded
as Relative transforms
25
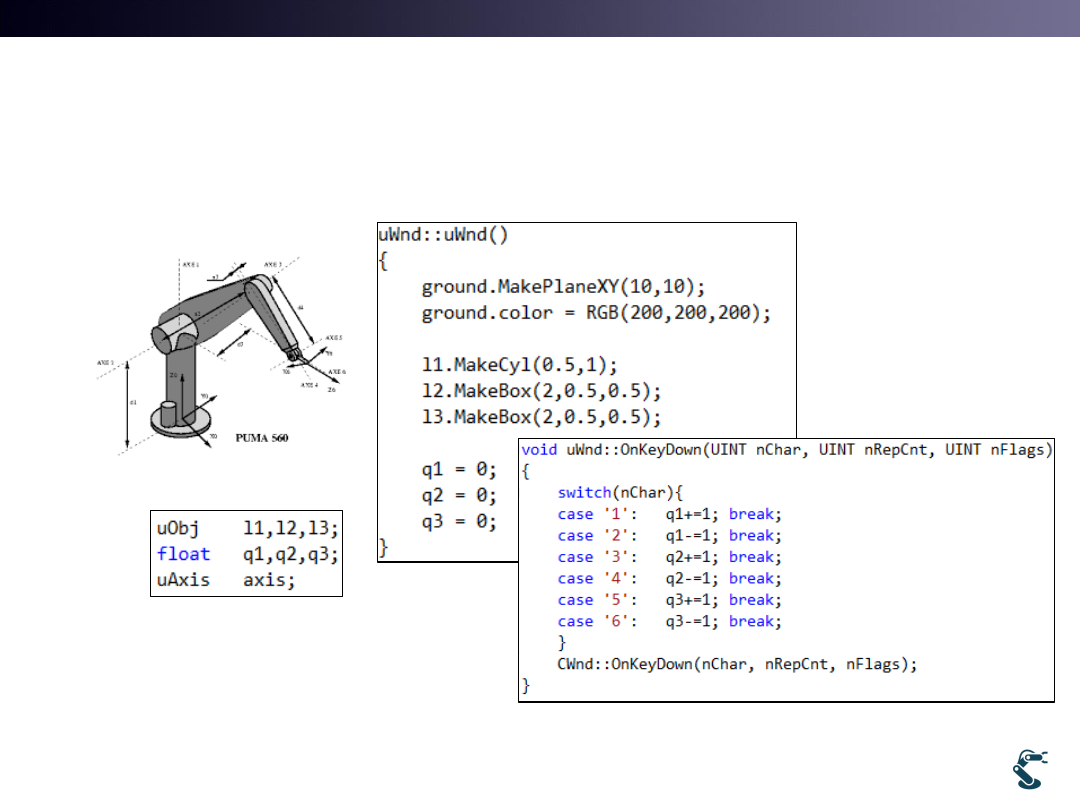
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
3 DOF PUMA
example
• One Cylinder and two boxes for 3 DOF PUMA.
• Key 1 & 2 for q1, 3 & 4 for q2, 5 & 6 for q3 rotation
26
uWnd.h
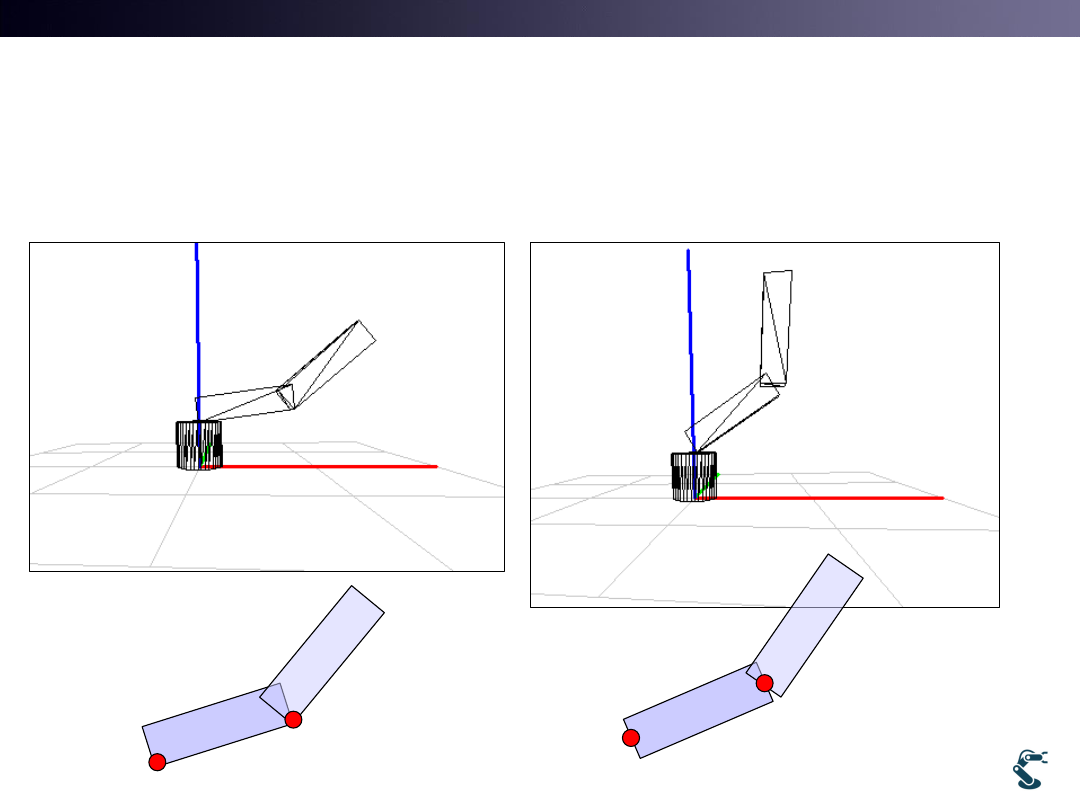
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Demo: puma.exe and puma2.exe
27
Rotation axis
Rotation axis
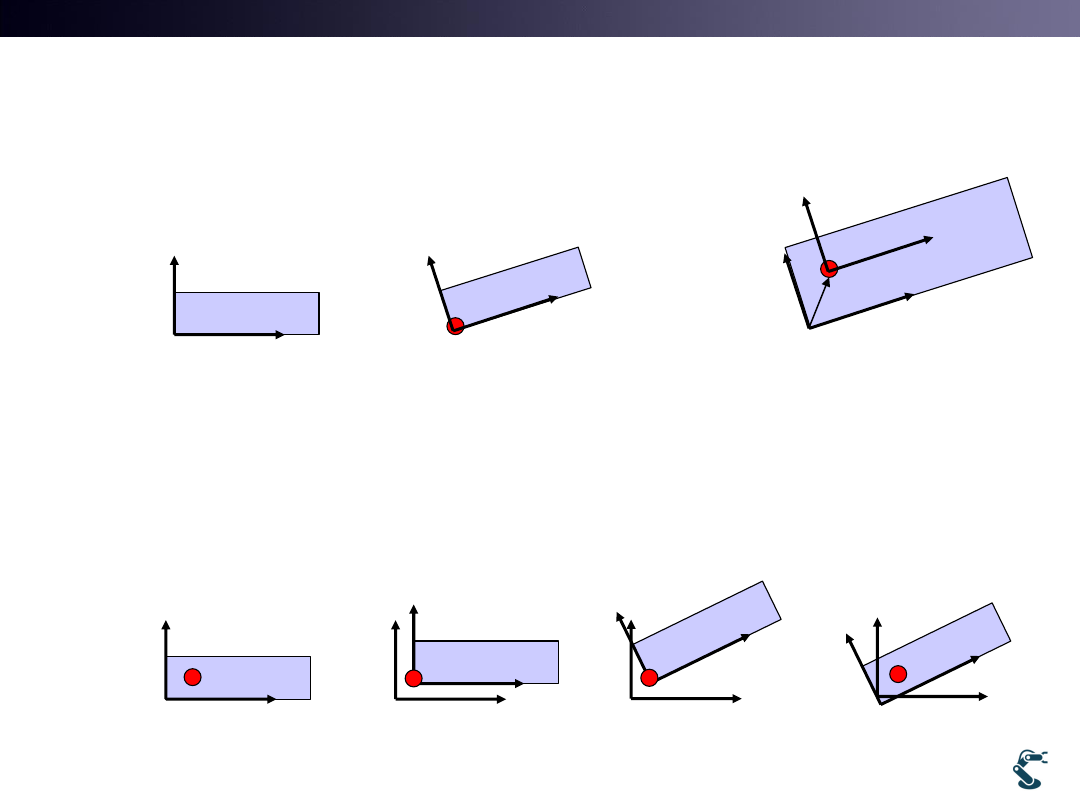
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Pivotal Rotation
How we rotate object at Other Positions
28
Original
object
Rotation at an origin
Rotation at the Pivot
HT
Trans
Rot
Trans
H
H
H
H
Original
object
Move to
Red point
Rotate at
the red pivot
Move back
to origin
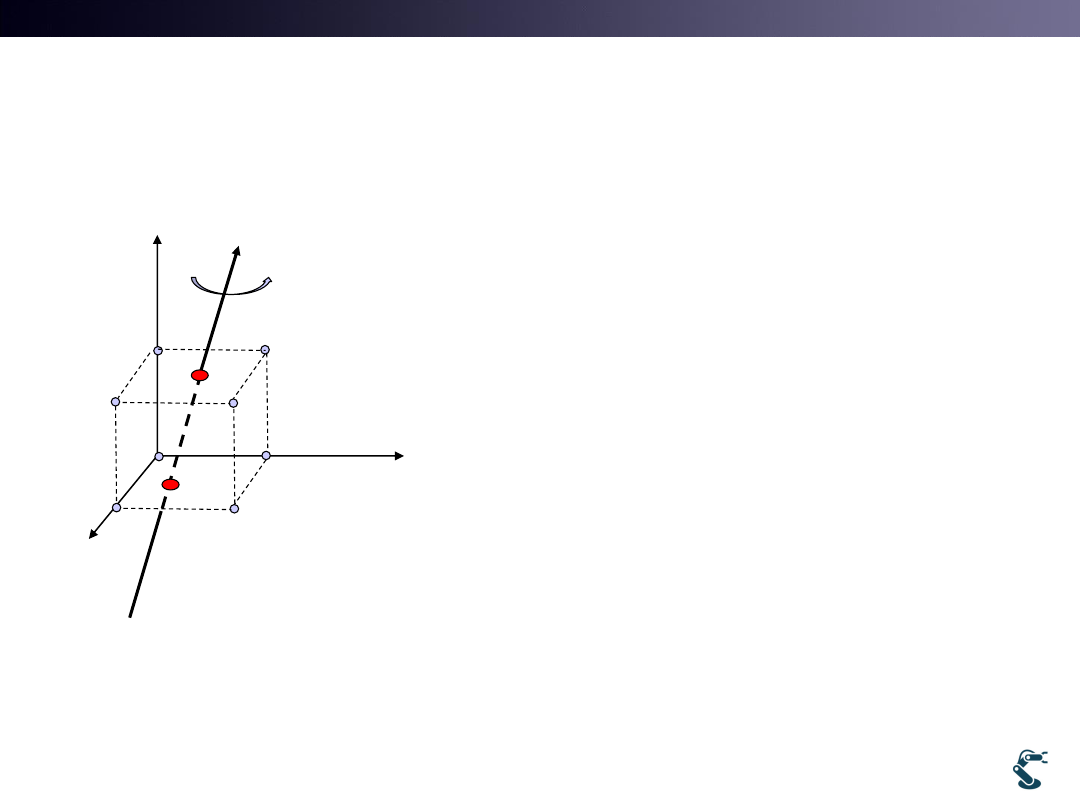
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Complex Pivotal Rotation
29
z
x
y
Trans
Rot
Trans
H
H
H
H
1. Pivotal point has only translation
2. Pivotal point has translation and
Rotation ( very complex)
1
p
Rot
p
H
H H
H
• When Pivotal point transform is very complex,
We need another method, Quaternion.
T&C LAB-AI
Example of Multiple Object
4
30
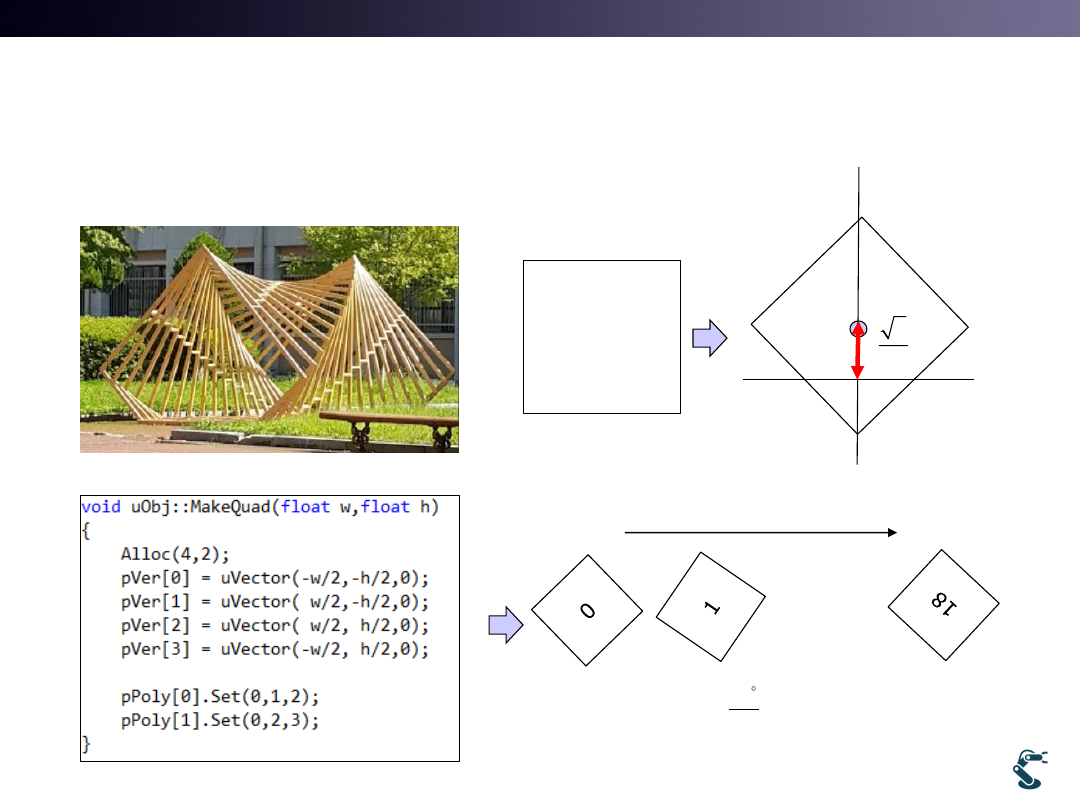
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
3Dim. Sculpture
Rotation of 19 Rectangles
31
2
2
2
2
2
2
1st quad
19 quad
90deg. rotation
90
18
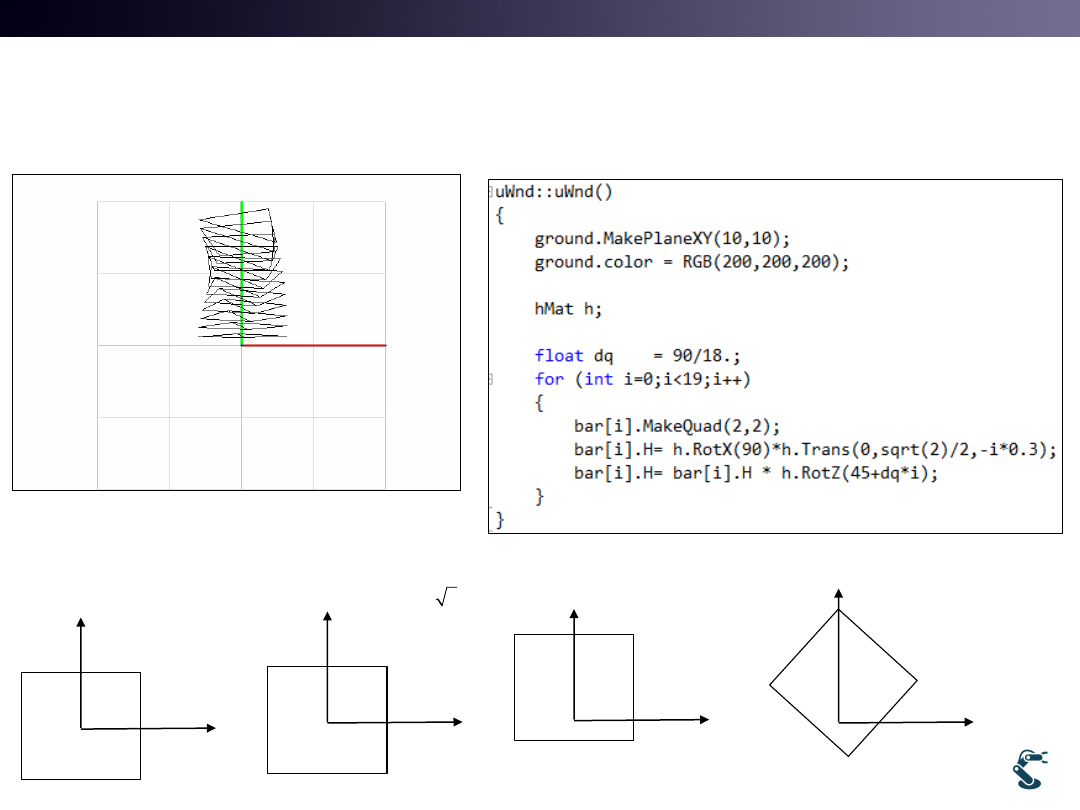
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Ex) uWnd-41-Sculp
32
x
y
z
(90)
RotX
z
(0, 2 / 2, 0.3 )
Trans
i
z
(45
* )
RotZ
dq i
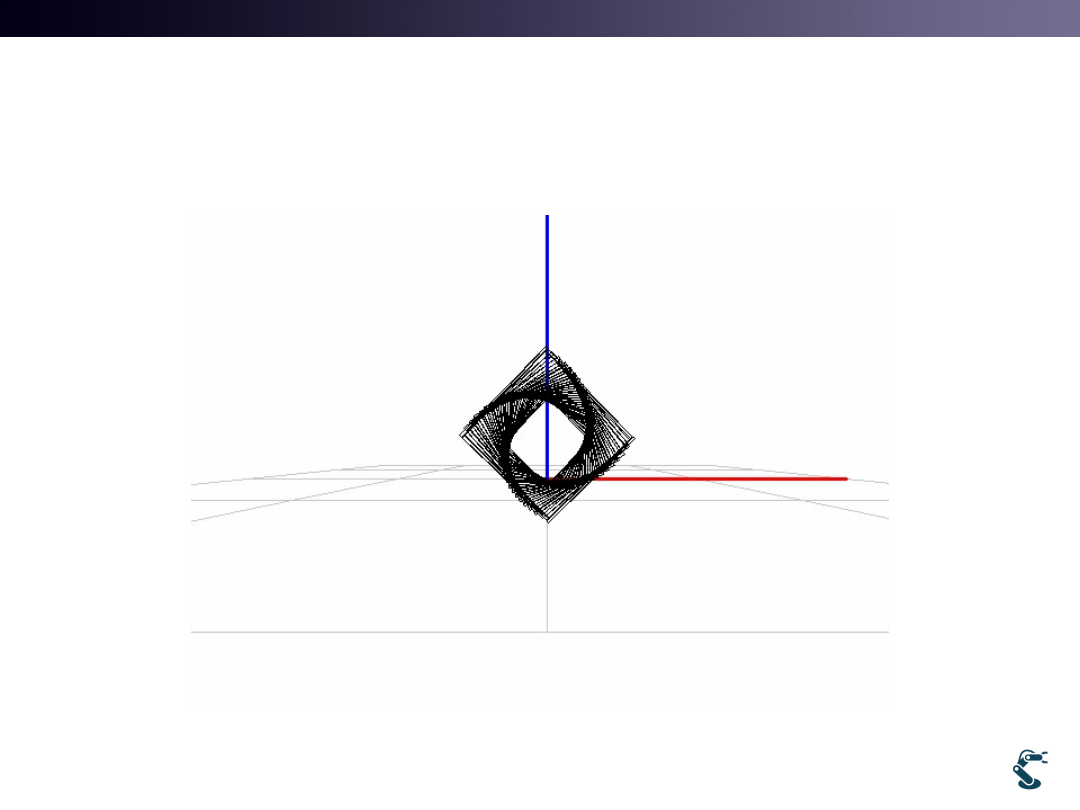
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Example
uWnd-42-Sculp2-Ans
33
Clipping with Plane will be covered later
T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
Event Programming for avoiding Flickering
uWnd-41-Sculp-Flickering
• Redraw() requires,
– obj.update() for projection
– Cam.R must be updated.
• Flag bRedraw is used
– When mouse moves or
key is pressed,
– bRedraw = TRUE to wait
for calling Redraw()
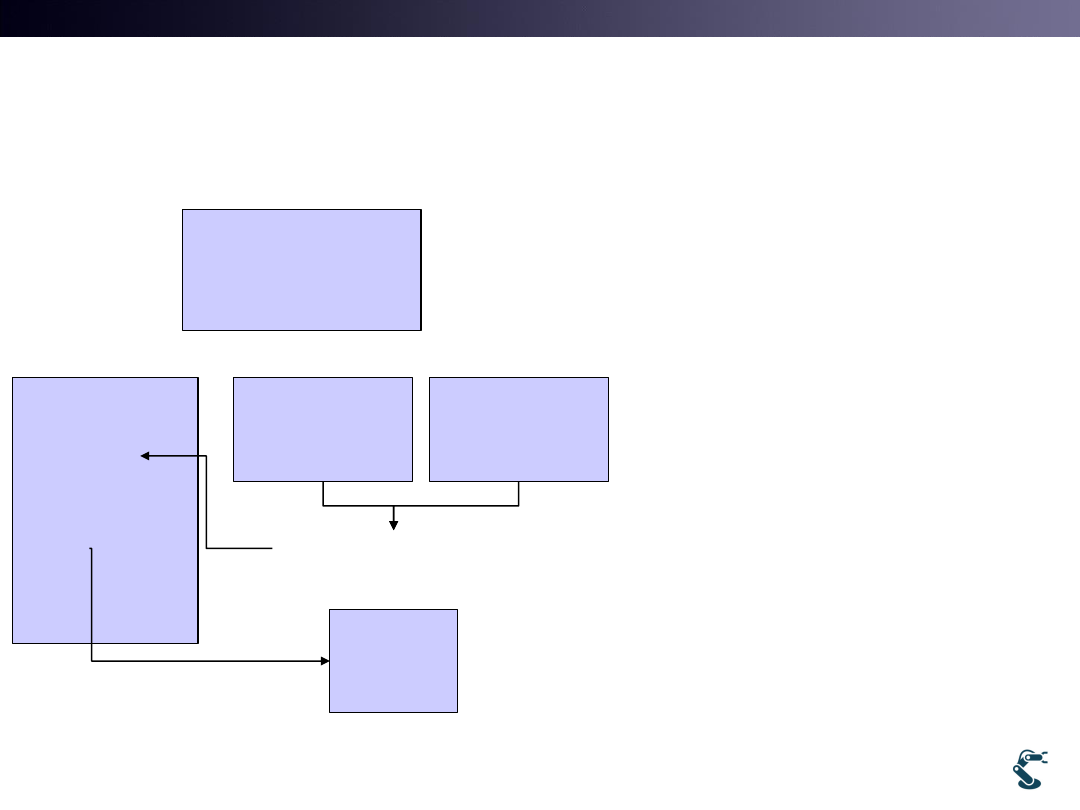
34
uWnd::uWnd
Initialize Modeling
Box.MakeBox(a,b,c)
Run
If (bRedraw)
{
Box.Update()
bRedraw=FALSE
Redraw()
}
onMousemove
onKeyDown
bRedraw=TRUE
onDraw

T&C LAB-AI
Dept. of Intelligent Robot Eng. MU
Robotics
35
Run() will
update
objects
Call onDraw()